Carbon capture & storage (CCS)
Ongoing Projects
Impact Fellow/Core
- Redesigning amine-based CO2 capture materials (Obi)
- An MIT research team spanning Materials Science (DMSE), Chemical Engineering (ChemE), Mechanical Engineering (MechE), and Chemistry collaborates to develop a class of energy-efficient, amine-based CO2 capture sorbents.
Seed
2022
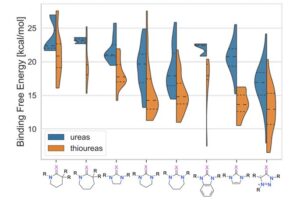
- Broad screening of CO2 binding (Gomez-Bombarelli)
- Exploring the combinatorial design of energy efficient capture solvents with tunable electronics properties using high throughput DFT.
- Energy transfer mechanisms (Gallant)
- Synthesis and experimental testing of promising amine candidates for CO2 binding strength and other performance metrics. Investigating electrochemical capture and release and efficient energy transfer mechanisms at ambient temperatures.
- Semi-automated synthesis of new molecules for carbon capture (Coley)
- Working to “close the loop” on machine learning-guided chemical synthesis using high throughput automation. Focused on mapping out the reaction space for synthetic route optimization and diverse library synthesis of CO2 capture candidates.
- Fundamental redox events at CO2 (Gilliard)
- Investigating the chemical oxidation and reduction of CO2 stabilized by organic ligands, and developing new strategies for CO2 utilization.
- Kinetic oxidation modeling (Green)
- Has built machine learning models for oxidative degradation of organic molecules and trained it on >150,000 transition state calculations (DFT). Testing model on candidate amines for CO2 capture.
Contact Us
Get in touch with the MCSC
If you would like more information, please e-mail mcsc@mit.edu.
Who’s studying this
MCSC Impact Fellow